Apache Spark is the hottest thing to happen to big data analytics yet and Tableau is the one of the hottest data visualization and discovery tools out there. Pair them together and you got a potential game changer in the field of big data analytics and visualization.
Tableau 9 is supported to be working with Spark but the setup isn't exactly straight forward, well not until you set the backend components setup correctly.
Why a hitchhiker's guide? Because its hitchhiked using multiple sources to compile a consolidated working guide that should help you get up and running with Tableau on a Spark cluster via SparkSQL. With that out of the way let's move on.
The Technology Stack
With a rapidly evolving open source ecosystem the Apache Hadoop and Spark has multiple stable and active versions. The below technology stack is what we've tested to be working with the Tableau integration.
- Hadoop 2.6 or later
- Hive
- mySQL - for housing the Hive metastore_db (more on this later)
- Spark 1.4 or later
- Tableau Desktop 9 or later
- Spark ODBC driver
Hadoop 2.6
In order to get all the Hive functionality working, you will need to be sure you are on Hadoop 2.6 or higher. There are work arounds to make this work on earlier Hadoop distributions, but its not worth the effort. Doing a Hadoop upgrade is far simpler. Since the Hadoop upgrade is in itself an extensive process, I am leaving it out of this post.
Hive Setup
Once you have installed or upgraded to Hadoop 2.6, you will need to install Hive. Start by downloading the latest stable version, unzipping the distribution and linking.
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump# wget http://mirror.cc.columbia.edu/pub/software/apache/hive/stable/apache-hive-1.1.0-bin.tar.gz
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump# md5sum apache-hive-1.1.0-bin.tar.gz
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump# tar -xzf apache-hive-1.1.0-bin.tar.gz
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump# mv apache-hive-1.1.0-bin /srv
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump# chown -R hadoop:hadoop /srv/apache-hive-1.1.0-bin
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump# ln -s /srv/apache-hive-1.1.0-bin /srv/hive
Setup hive specific environment variables
vim .bashrc
--# Configure Hive environment
export HIVE_HOME=/srv/hive
export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin
--## Resolve hive error due to hadoop using jline 0.9x whereas hive upgraded to Jline2
export HADOOP_USER_CLASSPATH_FIRST=true
There are a couple of other configurations, but we will deal with that later.
MySQL Setup
The default configuration of Hive comes with an embedded Derby Datastore, however it has a few limitations. Firstly it does not scale up well for any kind of production deployment. Next it also does not support shared connections every well. If we are going to connect with Tableau, we will need this. Assuming we have mySQL already installed on your system , you can configure it with Hive as below
Login to mySQL as the root user, create the metastore_db, the hive user account and the required privileges
mysql -u root -p
mysql> CREATE DATABASE metastore_db;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE USER 'hiveuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'hive123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT all on *.* to 'hiveuser'@localhost identified by 'hive123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
You will also need download the mySQL java connector from here, extract and copy it to your $HIVE_HOME/lib
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump/mysql-connector-java-5.1.36# cp mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar /srv/hive/lib/
root@XXXXX:/d01/swDump/mysql-connector-java-5.1.36# chown hadoop:hadoop /srv/hive/lib/mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar
Lastly create a hivesite.xml file in your $HIVEHOME/conf with the following entries. Replace the hive user and password with the appropriate values.
<configuration>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://localhost/metastore_db?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true</value>
<description>metadata is stored in a MySQL server</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
<description>MySQL JDBC driver class</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>hiveuser</value>
<description>user name for connecting to mysql server </description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>hive123</value>
<description>password for connecting to mysql server </description>
</property>
</configuration>
That's it you are all set(well almost). The next time you login to the hive shell, it should connect to the mySQL metastore_db and all objects will stored with that. You can start loading the test data.
hive> create table testaadh(state String, district String, gen int,reject int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' stored as textfile;
OK
Time taken: 1.526 seconds
hive>
hive> LOAD DATA INPATH '/user/samx18/tempdata.csv' INTO TABLE testaadh;
Loading data to table default.testaadh
Table default.testaadh stats: [numFiles=1, numRows=0, totalSize=552089, rawDataSize=0]
OK
You can query the mySQL metastore_db directly to check your hive tables are scuessfully created.
mysql -u hiveuser -p metastore_db
mysql> select * from TBLS;
+--------+-------------+-------+------------------+--------+-----------+-------+-------------+---------------+--------------------+--------------------+
| TBL_ID | CREATE_TIME | DB_ID | LAST_ACCESS_TIME | OWNER | RETENTION | SD_ID | TBL_NAME | TBL_TYPE | VIEW_EXPANDED_TEXT | VIEW_ORIGINAL_TEXT |
+--------+-------------+-------+------------------+--------+-----------+-------+-------------+---------------+--------------------+--------------------+
| 1 | 1441400778 | 1 | 0 | hadoop | 0 | 1 | hivetest | MANAGED_TABLE | NULL | NULL |
| 6 | 1441410858 | 1 | 0 | hadoop | 0 | 6 | testaadh | MANAGED_TABLE | NULL | NULL |
+--------+-------------+-------+------------------+--------+-----------+-------+-------------+---------------+--------------------+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Spark Setup
Make sure you have spark 1.4 or later setup on your Hadoop cluster, if not you can use the instructions here to get it setup.
To complete the spark setup with hive you will need to copy your hive-site.xml to your $SPARK_HOME/conf
$ cp $HIVE_HOME/conf/hive-site.xml $SPARK_HOME/conf/
Connect to your favourite Spark shell (pyspark in our case) and test the connection to the Hive table using the Spark Hive context. Depending on your spark build your hive context may or may not have been built for you.
>sqlContext = HiveContext(sc)
>results = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM testaadh")
>
Once you have confirmed you can access the hive tables via SparkSQL, start the Spark Thrift server. This will enable Tableau to make connection and run SparkSQL queries.
hadoop@XXXXX:~$ cd $SPARK_HOME/sbin
hadoop@XXXXX:/srv/spark/sbin$ ./start-thriftserver.sh
starting org.apache.spark.sql.hive.thriftserver.HiveThriftServer2, logging to /srv/spark-1.4.1-bin-hadoop2.6/sbin/../logs/spark-hadoop-org.apache.spark.sql.hive.thriftserver.HiveThriftServer2-1-XXXXX.out
Test connectivity to the Spark Thrift server using beeline
hadoop@XXXXX:~$ cd $SPARK_HOME
hadoop@XXXXX:/srv/spark$ ./bin/beeline
Beeline version 1.4.1 by Apache Hive
beeline> !connect jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
scan complete in 2ms
Connecting to jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
Enter username for jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000:
Enter password for jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000:
Connected to: Spark SQL (version 1.4.1)
Driver: Spark Project Core (version 1.4.1)
Transaction isolation: TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000>
Desktop Setup
Your server components are now setup and you can move to the desktop setups.
Download and install the following
Open Tableau, and create a new data source. Choose SparkSQL as the server type and fill in the details for your Spark Thrift server
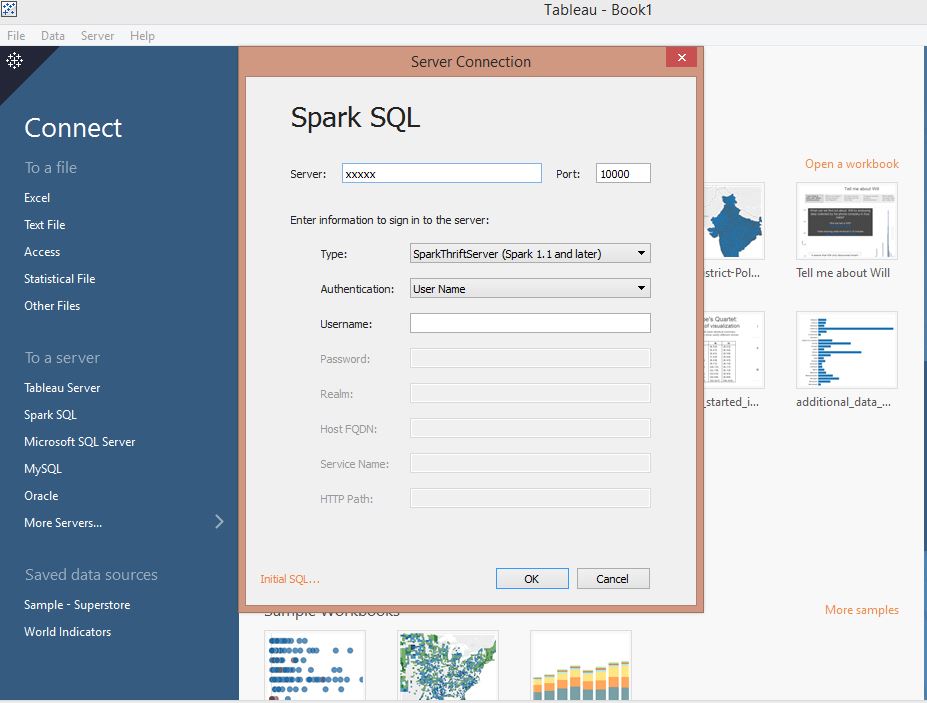
Browse to the default schema and you should see be able to see your Hive Hadoop cluster tables.
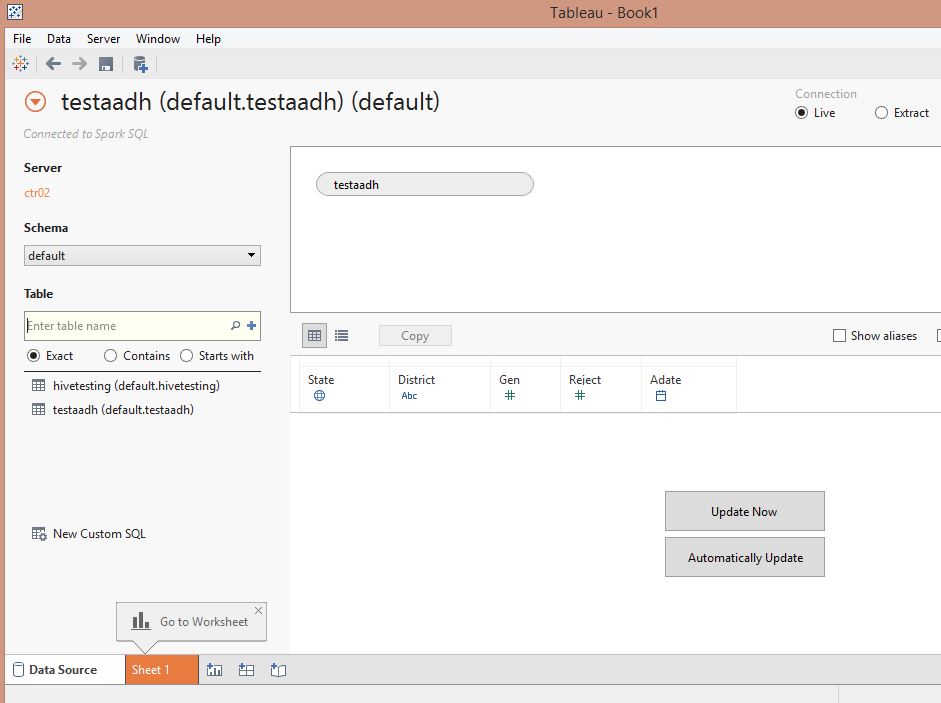
From here on you can use this as any standard datasource. Tableau will handle all your interaction via the SparkSQL analytic engine. Go ahead, have fun with Tableau + Spark.